
A relative path does NOT begin with " /" or " ~". Relative Pathname: A relative path is relative to the so-called current working directory.For example, " ~/Downloads/jdk/" is the same as " /Users//Downloads/jdk/" in macOS. That is, it starts with a " /" followed by all the sub-directories, separated with " /" leading to the file, e.g., " /usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.7.0_07/bin/".Īn absolute path can also begin with the current user's home directory (starts with "~"). Absolute Pathname: An absolute path begins from the root directory.The pathname can be specified in two ways: For example, in " /usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.7.0_07/bin/javac", the pathname is " /usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.7.0_07/bin/" and the filename is " javac". To reference a file, you need to provide the pathname (directory and sub-directories names) and the filename. In other words, ~/Downloads is the same as /Users//Downloads. You can use a special notation " ~" to denote your home directory.
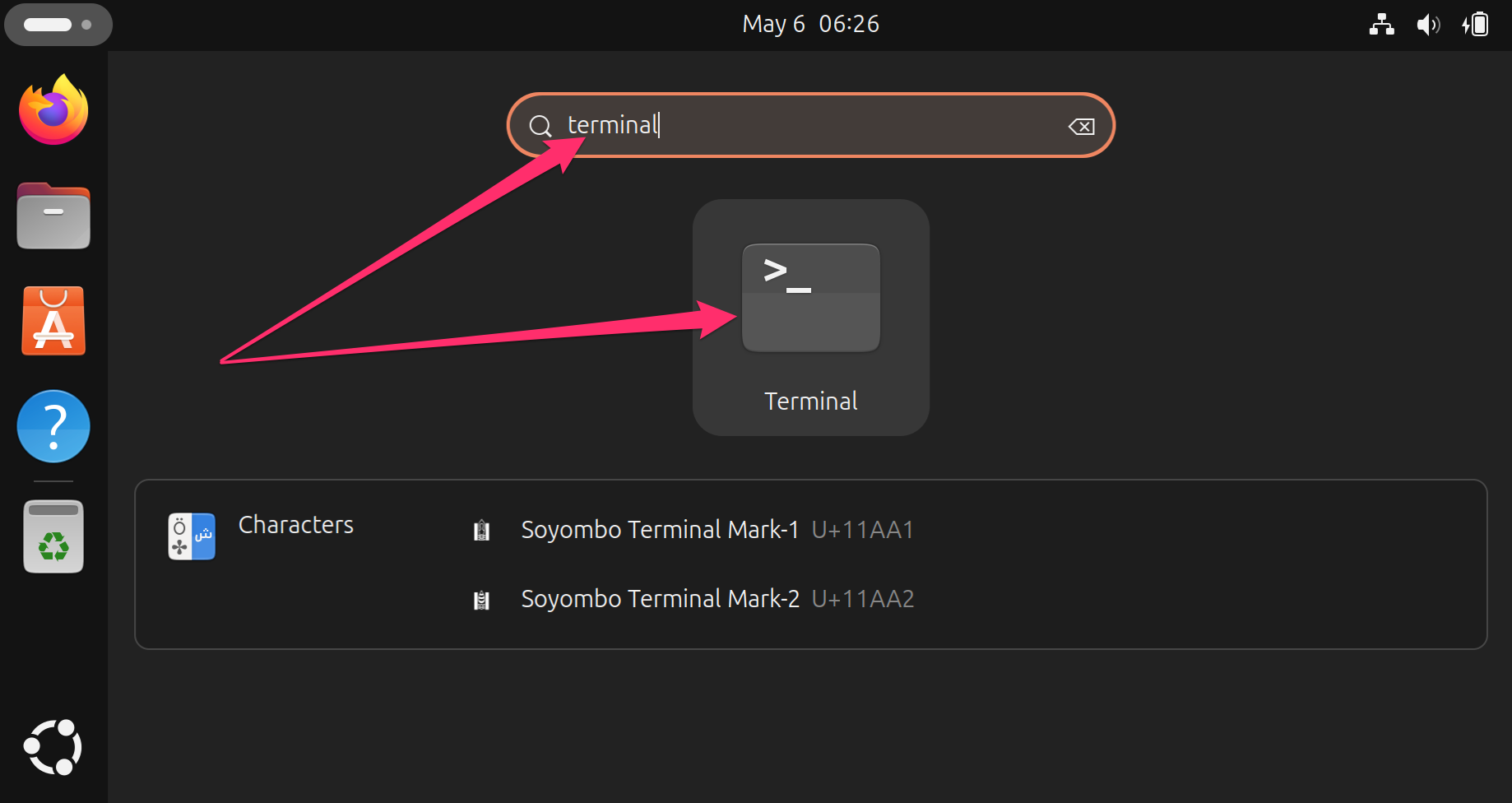
#UBUNTU OPEN TERMINAL FULL#
Their full filenames are /Users//Downloads, /Users//Documents, respectively. Your home directory ( /Users/) contains sub-directories such as Downloads, Documents. Users/peter, /Users/paul in macOS or /home/peter, /home/paul in Ubuntu. The users' home directories are allocated under /Users (for macOS), or /home (for Ubuntu), with a sub-directory name the same as the username, e.g. Each user on the system is allocated a directory for storing his files, known as home directory.
#UBUNTU OPEN TERMINAL MAC#
Unix is a multi-user operating system (although most of you, in particular the Mac users, use it as a single-user personal computer). Notes: Windows use " \" (back slash) as the directory separator, and may contain multiple root directories - one for each drive (e.g., c:\, d:\). Hard drives are mounted somewhere under the root directory. There is only one root directory for the entire Unix/macOS's file system. The sub-directories are also separated by a " /". The leading " /" (forward slash) denotes the root directory.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ubuntu-terminal-hotkey-34041f7fd039468dabf56a54fa801664.jpg)
Root Directory ( /)Ī file is identified via the directories and filename, e.g., " /usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.7.0_07/bin/javac". A sub-directory may contain sub-sub-directories and files. A directory may contain sub-directories and files.
The directories are organized in a hierarchical tree structure, starting from the root directory. Files are organized in directories (aka folders).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
